SSL Certificate
Deploy an SSL certificate to enable HTTPS encryption of websites, trusted identity authentication and prevent against data leaks or tampering during transmission.
Get SSL Certificate >Blog > Self-Signed Certificates: Are They Safe?
Tag:
Self-signed certificate
Private CA
Public CA
SSL certificate
1761:0
CatherineApril 25 2023

When browsing the internet, it's important to ensure that your data is secure and protected from potential threats. Typically, organizations use certificates issued by trusted CAs to secure external and internal communications. But there are also self-signed ones, generally used to secure internal system communications.
In this article, we will explain self-signed certificates in detail and try to be as clear and straightforward as possible. This article is recommended to all website owners.
Self-Signed certificates are created, issued, and signed by the organization or developer responsible for the website or the signed software. This can include SSL/TLS certificates, code signing certificates, and S/MIME certificates. Unlike SSL/TLS certificates that are verified by a trusted CA, self-signed certificates are not verified by any third-party CA. This means that the certificate holder is responsible for verifying their own identity and ensuring the security of the certificate. While self-signed certificates can provide some level of security, there are also some risks and limitations to consider.
Easy to issue: Issuing a self-signed certificate is a relatively straightforward process and can be completed anytime, without requiring any additional documentation or verification. This is very useful for testing and development.
Encrypted communication: Self-signed certificates, like other paid SSL/TLS certificates, provide encryption for online communication, which can help protect against eavesdropping and other forms of cyberattack.
Internal use: Self-signed certificates can be used for internal websites and services and software development phases, providing a level of encryption and security for internal communication.
It's important to note that while self-signed certificates can provide some benefits, they are not suitable for websites or services that collect sensitive information from users, such as e-commerce websites or online banking services since they cannot meet the security updates for discovered vulnerabilities or the certificate agility required for modern enterprise security today.
Lack of trust: Self-signed certificates are generally considered less trustworthy than certificates signed by CAs because they have not been vetted via a trusted process. Therefore, when users visit such a website, an error warning may be displayed (such as “error_self_signed_cert” or “sec_error_untrusted_issuer” or “err_cert_authority_invalid”) and users will have to click Accept the Risk and Continue in order to see the actual page.
Vulnerability to man-in-the-middle attacks: Self-signed certificates are vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks because they support extended validity periods and cannot perform security updates when new vulnerabilities are found. Therefore, it is easy for a third party to intercept the communication between the client and the server.
Lack of revocation: Self-signed certificates do not have a trusted mechanism for revocation, meaning that if a private key is compromised, there is no way to invalidate the certificate.
Less traffic: Visitors who encounter a security warning browsing your website may refrain from further visits and instead seek out alternative websites - possibly your competitors. This could result in a missed opportunity for business.
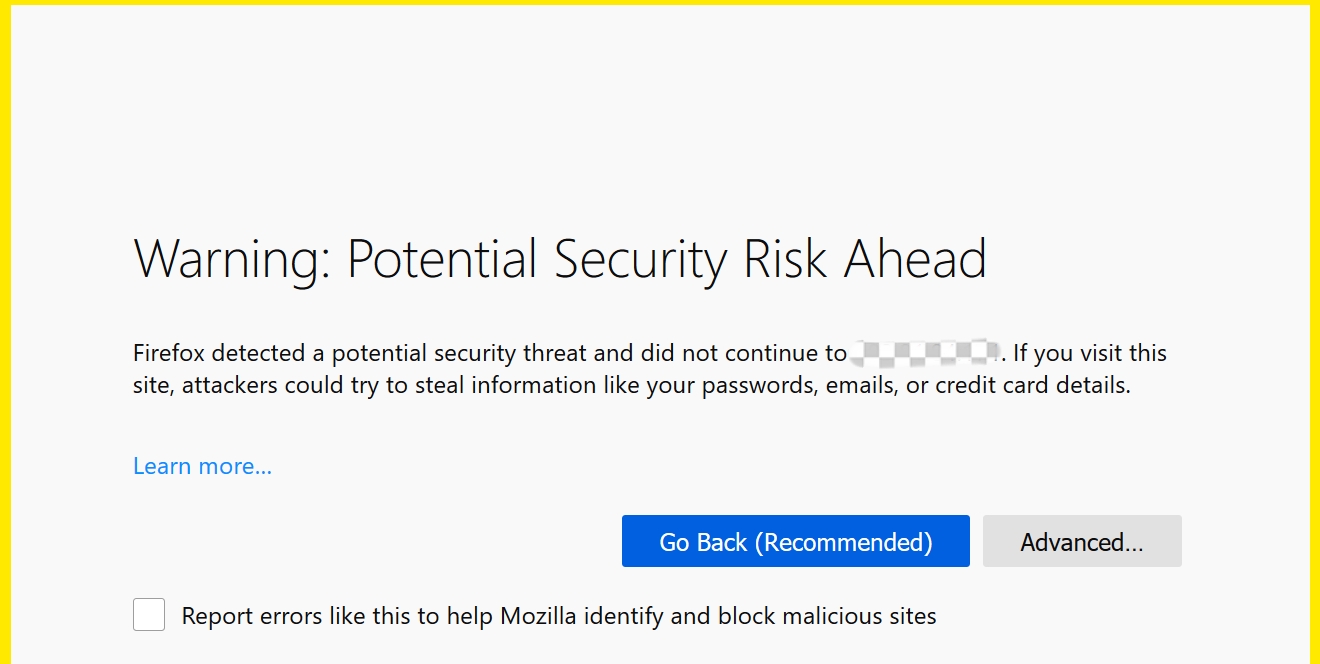
Validation: Trusted CAs validate SSL certificates before issuing them. This process involves verifying the certificate owner's identity, ascertaining their right to use the associated domain name, and meeting the requisite conditions for issuance. Conversely, self-signed certificates do not obtain third-party validation and are only signed by the entity who created them.
Trust: SSL certificates issued by trusted CAs are trusted by web browsers and email clients. Users accessing websites or emails secured by SSL certificates will not receive warnings or errors. Self-signed certificates, on the other hand, lack inherent trustworthiness and thus may cause compatibility difficulties or "error messages".
Vulnerability to cyberattacks: Self-signed certificates pose a potential vulnerability to cyberattacks inclusive of man-in-the-middle attacks, eavesdropping, and phishing. Due to the absence of verification from a trusted authority, adversaries can intercept and potentially compromise sensitive information transmitted across the internet. What's more, this information may be used for malicious purposes such as identity theft, financial fraud or other cyber crimes. Conversely, SSL certificates issued by trusted CAs utilize encryption algorithms that are profoundly intricate to break.
Of course, issuing a self-signed certificate is simple once you have your private CA, but it should not be used in an environment where security is critical. If you are securing a domain that is accessible to the public, it is best to choose a trusted public CA to issue certificates as their root certificates are stored in most browsers and trust repositories, making authentication easier. Public CAs issue most certificates and are sufficient for most use cases. To provide a product or service to the public and create a transparent environment, you'll need to obtain digital certificates from a trusted CA.
Many companies choose to use private CAs, especially if they issue a large number of certificates due to their size or the need for frequent reissuance. Running your own CA can be more cost-effective than paying for every certificate issued by a public CA.
But private certificates also have the obvious disadvantage that you have to set up and run the infrastructure yourself. Due to its substantial time and financial demands, this method is not used unless absolutely necessary.
NicSRS provides SSL certificates issued by the world's most trusted CAs such as DigiCert, Sectigo, and GlobalSign. It can be seen from the above that although self-signed certificates have certain benefits, in the long run, SSL certificates issued by trusted public CAs can help better avoid security risks such as user loss, data leakage, and man-in-the-middle attacks. NicSRS is committed to providing customers with high-quality services and best deals. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us and we will provide you with professional help.
RELATED
2025-04-24 16:08:08
2025-04-23 16:27:59
2025-02-25 14:33:23
2025-02-18 10:58:56
2025-02-14 14:41:07
Categories

Free SSL Tools
Top Posts
Comments