SSL Certificate
Deploy an SSL certificate to enable HTTPS encryption of websites, trusted identity authentication and prevent against data leaks or tampering during transmission.
Get SSL Certificate >Blog > What is the Relationship Between Domains, Websites and IP Addresses?
Tag:
Domains
Websites
IP Addresses
DNS
11635:0
CatherineJuly 21 2023

In this digital world, the seamless accessibility of websites has become an integral part of our daily lives. Yet, behind the simplicity of typing a domain name into a browser lies a complex web of connections that enable users to access their desired online destinations. The relationship between domains, websites, and IP addresses forms the foundation of the World Wide Web, facilitating the effortless navigation and retrieval of information from across the globe. In this article, we will discuss the relationship between them and explain the mechanisms that make the Internet function seamlessly.
Domain Name
A domain name is a human-readable address used to identify and locate a specific website on the Internet. It serves as a user-friendly, memorable representation of a website's actual IP (Internet Protocol) address, which is a series of numbers that computers use to communicate with each other. In essence, a domain name acts as the online "street address" that people can easily remember and type into their web browsers to access a particular website. For example, if we want to visit the official website of NicSRS, we enter "www.nicsrs.com" in the browser. This sequence of letters is the domain name of that webpage, representing its address on the Internet.
Website
A website is a collection of webpages and multimedia content hosted on web servers. It consists of HTML, CSS, JavaScript files, images, videos, and other resources that are presented to visitors when they access the corresponding domain name.
IP Address
The domain name mentioned above acts as an intermediary for accessing webpages. When people access a domain name, they are actually accessing the IP server address associated with that domain name. An IP address is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It serves as a unique identifier for that device on the network. IP addresses are expressed as a series of numbers separated by periods, such as “192.168.0.1” or “20001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334” (IPv6 format).
Once a domain name is registered, it needs to be mapped or connected to the web server where the website's files and content are stored. This mapping is done through DNS settings, which link the domain name to the server's IP address.
Domain Name System
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical system that translates human-readable domain names into their corresponding IP addresses. When a user enters a domain name into their web browser, the browser needs to find the IP address associated with that domain to establish a connection to the correct server hosting the website.
The DNS achieves this by using a distributed database that stores mappings between domain names and IP addresses. DNS servers around the world maintain this database and work together to resolve domain names to the correct IP addresses.
Domain to IP Address Resolution
When a user enters a domain name (e.g., "example.com") in their browser and hits Enter, the browser first contacts a DNS resolver (usually provided by the user's Internet Service Provider or a third-party DNS service).
- The DNS resolver looks up the domain name in its cache; if it's not found, it queries other DNS servers to find the corresponding IP address for that domain.
- Once the DNS resolver obtains the IP address (e.g., "192.0.2.100"), it returns it to the user's browser.
- The browser can then connect to the web server with the IP address "192.0.2.100" to request the website's content.
Therefore, domains serve as user-friendly aliases for IP addresses, allowing users to access websites without having to remember lengthy numerical sequences. The DNS acts as the translator between domain names and IP addresses, enabling users' devices to locate the appropriate web servers hosting the desired websites. The web servers, in turn, provide the content and resources that make up the websites, delivering them to users' browsers based on the domain name they entered. This seamless relationship between domains, websites, and IP addresses is fundamental to the functioning of the Internet and the accessibility of online content.
NicSRS provides an online free tool for querying DNS resolution records. This tool can quickly check the resolution speed of DNS mapping nodes in different regions of the world for your domain name, as well as DNS information, and can also query different types of domain name resolution records.
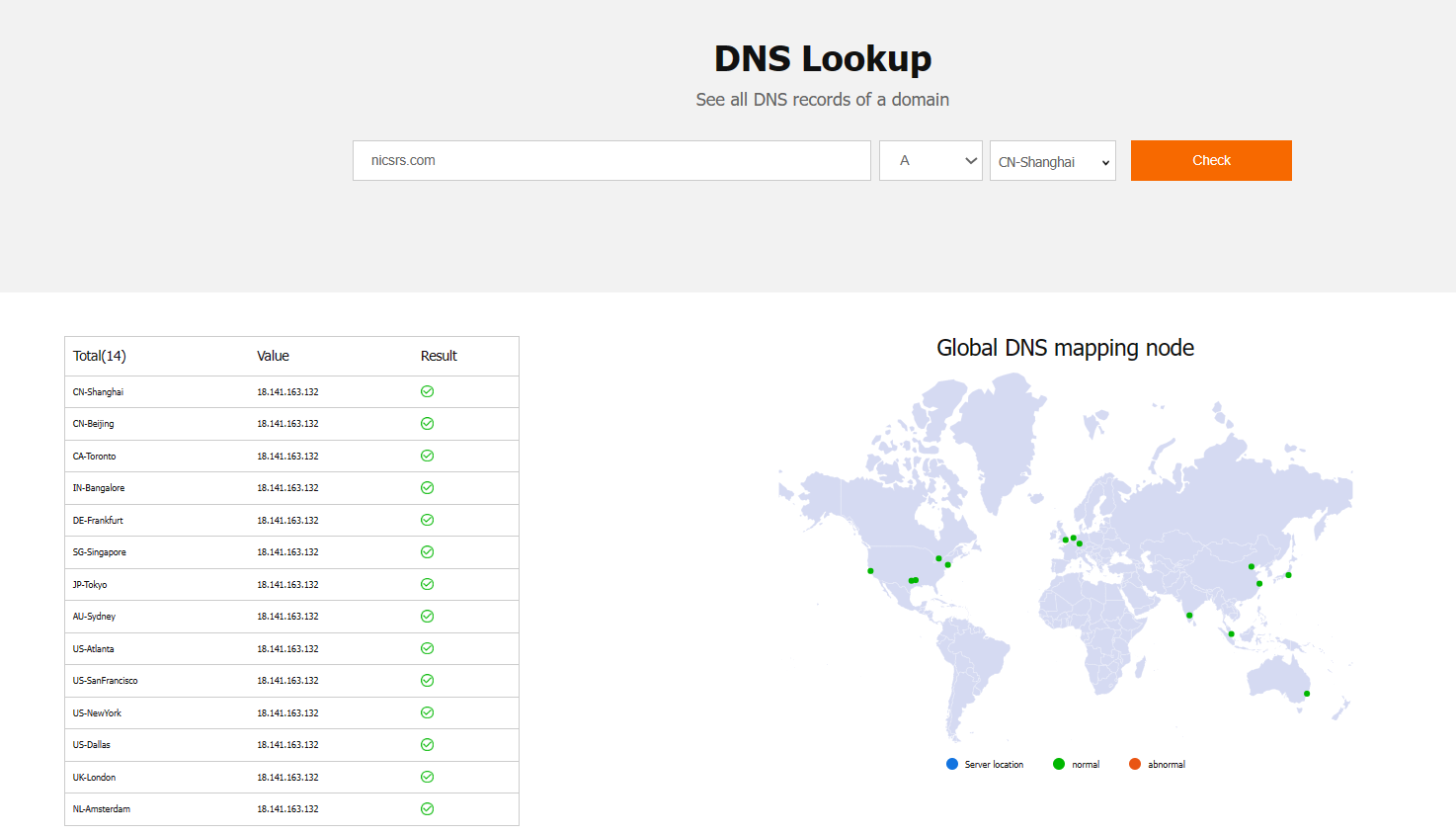
If you want to learn more about DNS, you can check out our previous article: "Demystifying DNS: A Guide to Understanding the Internet's Addressing System."
RELATED
2025-12-24 16:26:51
2025-12-18 15:37:42
2025-11-27 13:34:03
2025-10-16 11:03:19
2025-09-23 15:00:41
Categories

Free SSL Tools
Top Posts
Comments