SSL Certificate
Deploy an SSL certificate to enable HTTPS encryption of websites, trusted identity authentication and prevent against data leaks or tampering during transmission.
Get SSL Certificate >Blog > Server Certificates vs Client Certificates: What Are Their Differences?
Tag:
Server Certificates
Client Certificates
SSL Certificates
3188:0
CatherineOctober 9 2023
Server certificates, client certificates, root certificates, intermediate certificates, and so on - these specialized terms can be quite challenging for clients who have never dealt with digital certificates before to fully and accurately comprehend. You can refer to our previous writing about root certificates and intermediate certificates here. And this article will help to give you some idea of server certificates, client certificates and their differences. Serving as two fundamental types of certificates, server certificates and client certificates play a crucial role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data transmitted over the internet.
A server certificate, also known as an SSL/TLS certificate, is used to prove the authenticity of the server during the initial stages of establishing a secure connection with the client. In simple terms, using a server certificate enables different websites to provide identity authentication and ensure high-strength encryption security. Server certificates contain detailed authentication information, such as server information, the organization that issued the certificate, and a unique authentication file known as a public key. This means that server certificates ensure user verification of web server content and also imply that the established HTTP connection is secure.
SSL certificates protect your website's security by encrypting information and providing authentication. An SSL certificate consists of a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt information, and the private key is used to decrypt the encrypted information. When a client connects to a secure website or service, the server presents its certificate to the client's browser or application. The browser checks the server certificate against a list of trusted root certificates. If the server certificate is valid and issued by a trusted CA, a secure SSL/TLS connection is established, and data can be exchanged securely.
SSL certificates are categorized based on their functionality and validation levels. There are three validation levels, namely, domain validation (DV), organization validation (OV), and extended validation (EV).
Domain Validation (DV) Certificates: DV certificates are the most basic type of SSL certificates. They primarily focus on encrypting data between the user's browser and the server, providing basic security for online communication. DV certificates involve the least rigorous verification process. Certificate authorities (CAs) only confirm that the certificate applicant has ownership rights over the domain for which the certificate is requested. It is popular among forums, blogs, startups, and small businesses.
Organization Validation (OV) Certificates: OV certificates offer a higher level of security compared to DV certificates. In addition to encrypting data, they provide some assurance about the legitimacy of the organization behind the website. OV certificates involve a more thorough verification process. CAs verify both domain ownership and the legal existence of the organization requesting the certificate. OV SSL certificate is a good choice for enterprise website involving these pages such as registration, login, membership center, etc.
Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: EV certificates provide the highest level of assurance and security. They not only encrypt data but also offer the most stringent validation of the website's identity. EV certificates provide the highest level of assurance and security. Most of its verification steps are the same as those of the OV SSL certificate. Some certificate brands may also require applicants to fill in some additional documents to further verify the applicant s company and application information.
A client certificate, in comparison to the server certificate, is a digital certificate used to verify the identity of client-side users. It allows client-side users to authenticate their real identity when communicating with the server and can also be used for digitally signing and encrypting emails. It is applicable for strong user authentication in various secure systems, online applications, and network resources.
When a client initiates a connection with a server that requires client certificate authentication, the server requests the client to present its certificate. The client sends its certificate, which is signed by a trusted CA, to the server. The server then verifies the client's identity by checking the certificate against its list of trusted root certificates. If the certificate is valid and trusted, the client gains access to the server's resources.
The core of identity authentication is to verify who someone or some device is. Therefore, when we talk about client certificates or PKI certificates, we are referring to the use of X.509 digital certificates and public key infrastructure for remote identification of individuals and their devices in public communications. Such certificates are widely used in various scenarios in our daily lives, such as when logging into VPNs or sending emails to external organizations, and more.
In summary, client certificates are used to identify the true identity of devices or users and establish secure connections between both ends of the communication. This is a method of restricting system access to only authenticated users or devices. The following digital certificates have identity authentication capabilities:
- User certificates
- Device certificates
- Two-way authentication certificates
- S/MIME certificates
- Document signing certificates
S/MIME certificates: S/MIME certificates are primarily used for securing email communication. These certificates allow individuals to digitally sign and encrypt their emails, ensuring the authenticity of the sender and the confidentiality of the email contents. When an individual uses an S/MIME certificate to sign an email, it adds a digital signature to the message. This signature is unique to the certificate holder and serves as proof of their identity. Recipients can verify the signature using the sender's public key, ensuring the email's integrity and origin.
Document signing certificates: Document signing certificates are used to digitally sign documents and files, including PDFs, Word documents, and more. These certificates provide a verifiable digital signature to ensure the authenticity and integrity of the signed documents. When an individual uses a document signing certificate, it generates a digital signature unique to the certificate holder and attaches it to the document. Recipients or document users can verify the signature using the signer's public key to ensure the document has not been tampered with and that it originates from the claimed signer.
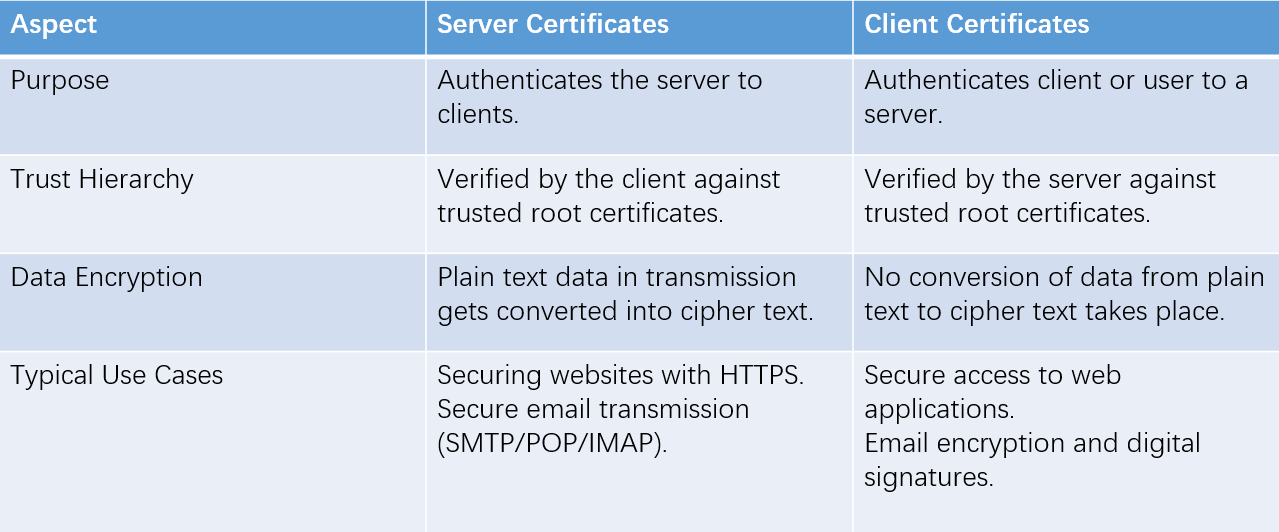
Client certificates and server certificates are integral components of secure communication in today's digital age. While client certificates authenticate users or devices to servers, server certificates ensure data confidentiality and server authenticity. Both certificates, issued by trusted CAs, play crucial roles in safeguarding sensitive information in a world where cybersecurity is of paramount importance. Understanding the differences and significance of these certificates is essential for individuals and organizations committed to maintaining the highest levels of security in their online interactions.
As a leading digital certificate provider, NicSRS provides customers with industry-standard client certificates and server certificates. NicSRS has SSL certificates from most brands and also provides S/MIME certificates and document signing certificates to ensure the security of customers' personal information and prevent any potential data leakage. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us and we will provide you with timely professional assistance.
RELATED
2025-02-25 14:33:23
2025-02-18 10:58:56
2025-02-14 14:41:07
2025-02-08 17:31:15
2025-01-20 14:47:16
Categories

Free SSL Tools
Top Posts
Comments