SSL Certificate
Deploy an SSL certificate to enable HTTPS encryption of websites, trusted identity authentication and prevent against data leaks or tampering during transmission.
Get SSL Certificate >Blog > Understanding the Distinction: Digital Signature vs. Digital Certificate
Tag:
Digital Signature
Digital Certificate
Certificate Authority
NicSRS
3951:0
CatherineJune 29 2023
In today's digital age, where data transmission and communication take place predominantly in the virtual realm, ensuring the security and integrity of digital transactions is of paramount importance. As organizations and individuals increasingly rely on digital platforms for exchanging sensitive information, the need for robust cryptographic measures has become imperative. Two fundamental components that play a vital role in securing digital communications are digital signatures and digital certificates.
While digital signatures and digital certificates may sound similar, they serve distinct purposes in the realm of cybersecurity. Understanding the differences between these two cryptographic elements is essential for implementing effective security measures, establishing trust, and safeguarding digital assets. In this article, we will introduce the differences between digital signatures and digital certificates. However, before we proceed, it is important for you to familiarize yourself with the definitions and some related concepts of digital signatures and digital certificates.
A digital signature is a cryptographic mechanism used to provide integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation to digital documents or messages. It serves as a digital equivalent of a handwritten signature and verifies the integrity of the signed content. Digital signatures are based on asymmetric key cryptography, where a private key is used to sign the document, and a corresponding public key is used to verify the signature.
The process of creating a digital signature involves applying a mathematical algorithm to the document using the signer's private key. This algorithm generates a unique digital fingerprint, or hash value, that is encrypted with the signer's private key. The resulting encrypted hash, along with the original document, forms the digital signature. When the document is later verified, the recipient uses the signer's public key to decrypt the encrypted hash and compare it with a recalculated hash value of the received document. If the two values match, the signature is considered valid, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of the document.
Digital signatures offer numerous advantages in today's digital landscape, providing enhanced security and authentication for digital transactions and communications. However, like any technology, they also have their limitations and potential disadvantages.
Security: Digital signatures provide a high level of security for digital documents and communications. They ensure the integrity and authenticity of the data by verifying the identity of the signer and detecting any unauthorized modifications to the document.
Authentication: Digital signatures provide strong authentication, as they are linked to the signer's unique digital identity. This helps verify the identity of the sender and ensures that the document has not been tampered with during transmission.
Efficiency: Digital signatures streamline and expedite document workflows by eliminating the need for printing, signing, and scanning physical documents. This improves efficiency, reduces costs, and saves time, particularly for remote or international transactions.
Legitimacy: It is provided by a government-authorized CA.
Dependent on Technology: Digital signatures rely on secure technology and encryption algorithms. If any vulnerabilities or weaknesses are discovered, it could undermine the effectiveness of digital signatures and raise security concerns.
Compatibility Issue: You need to ensure that the digital signature you are using is compatible with different operating systems.
User Adoption: The adoption and acceptance of digital signatures may vary among individuals and organizations. Some people may be unfamiliar with the technology or have concerns about its reliability or security. Educating users and promoting awareness are crucial for widespread adoption.
A digital certificate, also known as a public key certificate, is a digital document that authenticates the identity of an entity, such as an individual, organization, or a website. It is issued by CAs after verifying the identity of the entity and its public key.
The structure of a digital certificate is hierarchical, forming a chain of trust. At the top of the chain is the root certificate, self-signed by the CA. Intermediate certificates are then issued by the root certificate, and finally, end-entity certificates are issued by the intermediate certificates. This hierarchical structure ensures the authenticity and integrity of the entire certificate chain.
Digital certificates play a vital role in establishing secure communication channels, enabling secure browsing (HTTPS), email encryption (S/MIME), code signing, and various other digital transactions. They allow parties to verify the authenticity of each other's identities, ensuring secure and confidential communication.
Enhanced Security: Digital certificates provide a secure and tamper-proof way to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital information. They use cryptographic algorithms to ensure that the information remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
Authentication: Digital certificates serve as a means of verifying the identity of individuals, organizations, or devices in online transactions, effectively mitigating the potential risks of impersonation and fraudulent activities.
Non-Repudiation: Digital certificates incorporate digital signatures, which provide non-repudiation. This means that the signer cannot deny their involvement in a transaction or the authenticity of a document, as their digital signature acts as irrefutable evidence.
Wide Application: Digital certificates are widely used in various industries and applications. They are commonly employed in secure email communication, e-commerce transactions, online banking, document signing, and authentication for secure access to networks or systems.
Cost: Obtaining and managing digital certificates can involve cost considerations. Depending on the required security level and certificate type, there will be corresponding expenses for acquiring, renewing, and managing certificates.
Revocation Challenges: In certain cases, digital certificates may need to be revoked if they are compromised or if the associated private key is lost or compromised. However, the process of revocation and the distribution of updated certificate revocation lists (CRLs) can sometimes be challenging, potentially causing delays in the timely revocation of compromised certificates.
Dependency on CAs: Digital certificates rely on trusted CAs to issue and manage certificates. The trustworthiness and reliability of the CA play a crucial role in the overall security and validity of the digital certificates. If a CA is compromised or its practices are not secure, it can undermine the trust associated with the issued certificates.
So far the article has discussed the concepts, advantages, and disadvantages of both digital signatures and digital certificates. Both utilize the principles of public-key cryptography to verify identity, prevent against data tampering, and enhance communication security. So, what exactly are the differences between them?
Digital signatures and digital certificates are closely related but serve different purposes within the cryptographic ecosystem. A digital signature is used to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital data, while a digital certificate is used to bind an entity's identity to a public key and facilitate secure communication. Digital signatures are often used to provide additional trust and assurance in the identity of the signer.
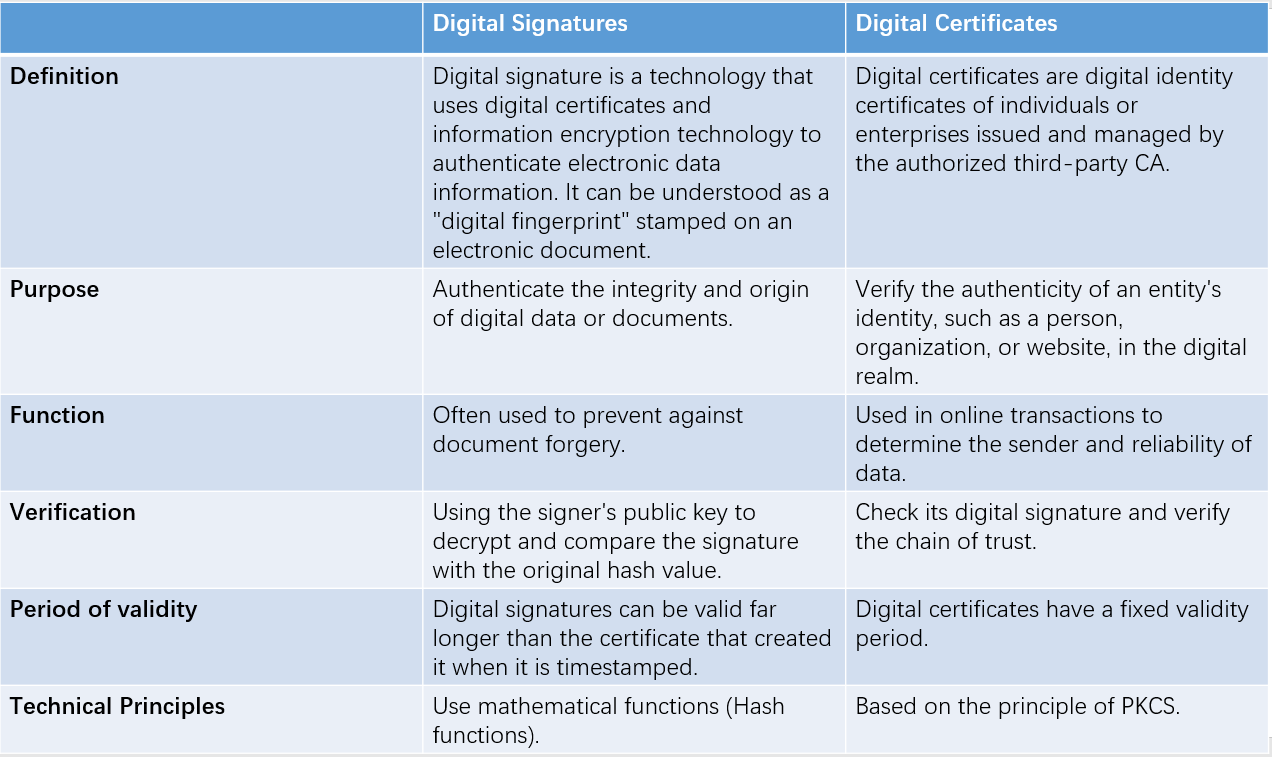
In summary, digital signatures and digital certificates are integral components of modern cryptographic systems. Digital signatures provide integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation to digital documents, while digital certificates establish the trustworthiness and ownership of public keys. Together, they ensure secure communication, protect against tampering, and validate the authenticity of digital transactions.
As a leading digital certificate service provider, NicSRS provides users with high-quality digital certificates to meet different needs. If you have any further questions, please feel free to contact us. We are committed to providing prompt and professional assistance.
RELATED
2025-12-18 15:37:42
2025-12-17 18:03:54
2025-11-27 13:34:03
2025-10-16 11:03:19
2025-09-23 15:00:41
Categories

Free SSL Tools
Top Posts
Comments