SSL Certificate
Deploy an SSL certificate to enable HTTPS encryption of websites, trusted identity authentication and prevent against data leaks or tampering during transmission.
Get SSL Certificate >Blog > Email Phishing: Securing Against It with S/MIME Certificates
Tag:
Email Phishing
S/MIME Certificates
NicSRS
1773:0
CatherineJuly 11 2023

Phishing is commonly performed through emails by impersonating banks or other reputable institutions and sending deceptive messages to recipients, enticing them to provide sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, ATM card PIN, or credit card details, in order to profit illicitly. Phishing is one of the most common tactics used in cyberattacks, accounting for approximately 90% of all data breach incidents. To combat this menace, S/MIME certificates issued based on best practices have made their way into a wider deployment.
This article introduces the common examples of phishing emails and the measures to prevent against such scams, helping you better identify and avoid phishing scams and enhance the security of online communication.
A phishing email refers to a deceptive email that tricks recipients into replying with account credentials, passwords, or other sensitive information to a specified recipient. Alternatively, it may direct recipients to visit a specially crafted webpage, often disguised as a legitimate website, in order to deceive them into providing personal and private information such as credit card or bank account numbers, account names, and passwords.
Unfamiliar or unusual tones and greetings
If you notice a sudden change in the writing style of a long-term business partner, it should raise a red flag. If a call to action follows the greeting, it is advised to maintain a skeptical attitude towards the sender's true identity.
Suspicious email addresses and fake links
You should verify the actual URL of the sender and the links within the email. This is often the quickest way to determine the authenticity of an email account. Instead of clicking on the links, hover your mouse over them and pay attention to any suspicious words or domain name extensions. If the email claims to be from Paypal.com but the link does not lead to Paypal.com, mark the email as spam and delete it.
Grammar errors
Most legitimate companies take great care to proofread their emails before sending them. If you notice obvious spelling or grammar mistakes in an email, it should raise concern as it could be a phishing attempt. For one, legitimate companies know how to spell. For another, bad grammar can be on purpose because hackers tend to target the less educated users.
Request for credentials and payment information
A seemingly official email may ask you to visit a fraudulent login page and submit your personal data or even request payment to resolve an issue mentioned in the email. To avoid becoming a victim of this kind of elaborate scam, access the mentioned site by typing in the URLs instead of clicking on the provided links.
No digital signature
A digital signature verifies the genuine identity of the sender. Similar to SSL certificates, S/MIME certificates support end-to-end encryption of email communication. You can check the status of incoming emails on your client by clicking the red badge icon on the right side of the email. A green checkmark displayed indicates that the email has been digitally signed by a trusted CA. If a red warning is displayed, it indicates possible tampering or an invalid certificate. If you cannot find the icon, exercise caution regarding the authenticity of the sender's identity.
1. CEO fraud and executive phishing emails: These emails mimic a leader or authoritative figure, adopt a formal tone, and often involve requests for account and password information.
2. Email account-related issues: Phishing emails in this category typically appear as notifications regarding "unusual account activity," "storage capacity upgrades," "security alerts," or "email configuration updates."
3.Name spoofing: These emails may adopt sender names such as "Email Administrator," "XX Customer Service Center," or "Service Email" or other names to trick recipients into thinking the email comes from an entity they know. Such emails may claim that the email accounts have expired or report security vulnerabilities.
4. Fake bounce-back emails: Phishing emails designed to resemble bounced emails or those sent by a "Postmaster."
5. Unrequested attachments: Emails with unrequested attachments often include message that invokes sense of urgency or fear to convince recipients to click on the attachments. These attachments may contain executable programs, such as viruses, or direct recipients to input account passwords.
6. Purchase order scam: These phishing emails typically feature minimal product requirements, descriptions, and specifications. They focus on order and payment confirmation, enticing recipients to disclose sensitive information.
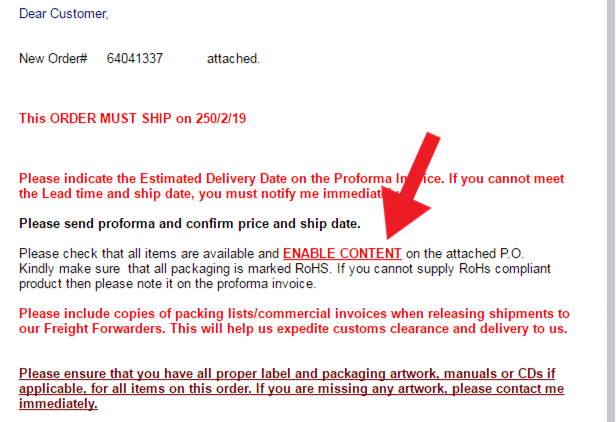
In order to effectively protect against phishing attacks, it is important for users to develop good email habits and remain cautious when encountering emails that contain hyperlinks or buttons. However, the most effective method to safeguard against phishing is by utilizing S/MIME certificates, which ensure email security through data encryption, identity authentication, and signature technology.
Email signing is enabled by importing and installing an S/MIME certificate into email clients. When a sender digitally signs an email, the recipient can verify the sender's true identity, thereby effectively thwarting phishing attempts. This also prevents any tampering with the email during transmission, ensuring the authenticity, integrity, and validity of the email content, thereby significantly enhancing trust in the emails received.
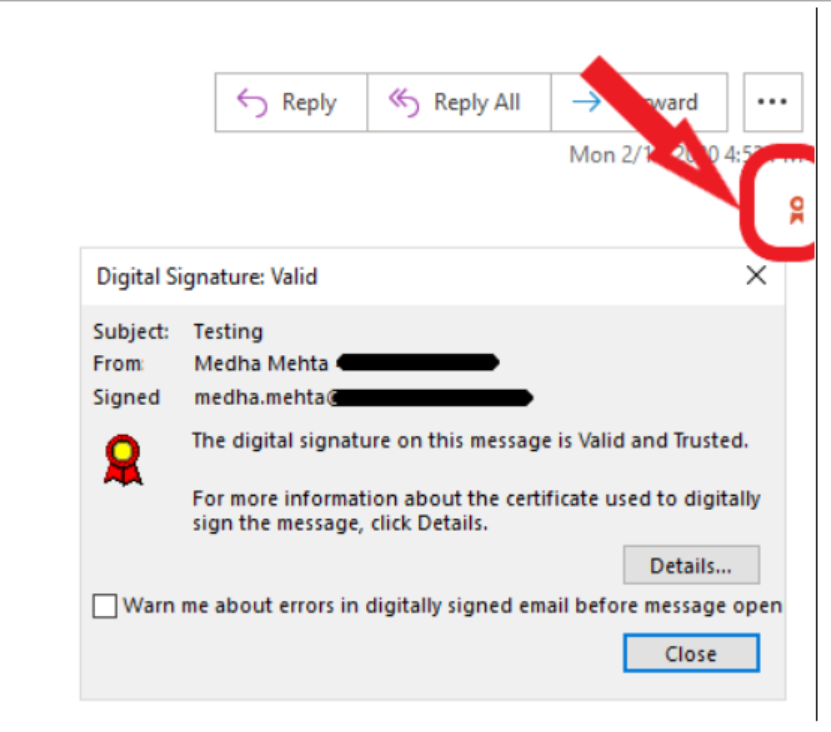
As the picture shows, emails signed with an S/MIME certificate will display the verified signer's identity and a small ribbon icon will be displayed in the upper right corner of the email. By clicking on the icon, recipients can access the details of the certificate, enabling them to identify and avoid falling victim to email phishing scams.
As a leading digital certificate provider, NicSRS provides customers with industry-standard S/MIME certificates to ensure the integrity and authenticity of emails. It is worth noting that besides digital signatures, S/MIME certificates also offer the added benefit of email content encryption, ensuring the security of email information and preventing any potential data breaches. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us and we will provide you with timely professional assistance.
RELATED
2025-04-24 16:08:08
2025-02-25 14:33:23
2025-02-18 10:58:56
2025-02-14 14:41:07
2025-02-08 17:31:15
Categories

Free SSL Tools
Top Posts
Comments